Towards a novel therapeutic approach for Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the most prevalent neurological disorder after Alzheimer’s pathology. Physical symptoms, such as the inability to move, are caused by the progressive degeneration of dopamine neurons located in the substantia-nigra. There is currently no cure for PD nor is there an alternative to current suboptimal treatments.
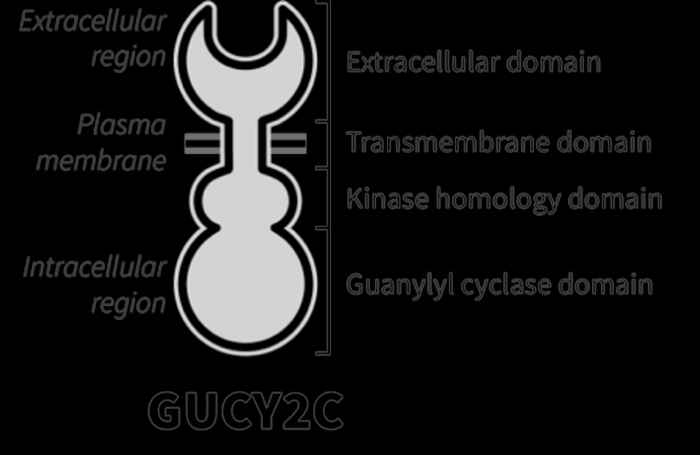
In the quest to find novel therapeutic approaches to treat PD, the researchers have identified the Gucy2c receptor as a potential target. This receptor improves clinical symptoms comparable to levodopa in an animal PD model, whereas complementary studies have shown that the Gucy2c receptor also protects dopamine neurons.
Due to its specific expression in the substantia-nigra, therapeutically targeting Gucy2c would have no side-effects, restore dopamine levels and prevent further neurodegeneration.